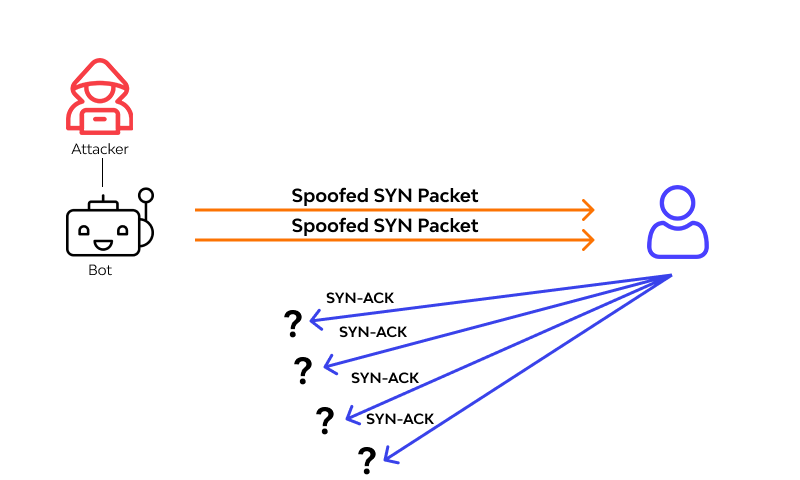
How to Manipulate a Cellphone Connection via TCP Manipulating a cellphone connection using the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) involves
-
-
Hacker Inc Discovering infidelity in a relationship is painful, but technology can help uncover the truth with discretion and efficiency. From
-
How Easily Can TikTok Be Hacked: A Full Exploitation Analysis TikTok, the global social media giant, boasts over a billion monthly active users
-
Black hat hackers deploy a vast array of techniques to exploit systems, networks, and individuals for financial gain, disruption, or malicious
-
Personalized Hacking Masterclass with Tony Capo: Social Engineering, Mobile Technology, and Exploitation Connect on Telegram. Staying ahead of
-
What is DVIUS? DVIUS, or Divergent Virtual Integrated Utility System, is an #AI-powered cybersecurity suite specializing in offensive operations,
-
Educational Article: Understanding Instagram’s Security Features and How Ethical Hackers Analyze Them Instagram, with over 2 billion monthly active
-
WhatsApp, with over 2 billion users globally, is one of the most popular messaging platforms, relied upon for personal and business communications.
-
DVIUS Leads the Charge in Autonomous Offensive Cybersecurity for Businesses With the advancement of technology, businesses now face an ever-evolving
-
Apple’s iOS is renowned for its robust security architecture, designed to protect user data and ensure device integrity. Understanding how iOS